
Teacher Leadership for School-Wide English Learning, First Edition
Contents
Chapter 2: Teacher Professionalism, Distributed Leadership, and Peer Coaching
Chapter 3. The SWEL Model of Academic Language Instruction
Chapter 4: Teacher Dispositions Needed to Effectively and Respectfully Serve English Learners
Chapter 5: Teacher Knowledge Needed to Effectively and Respectfully Serve English Learners
Chapter 6: Teacher Skills Needed to Effectively and Respectfully Serve English Learners
Chapter 7: Setting Up Teachers for Success
Chapter 8: Drafting an Annual SWEL Action Plan
Appendixes
Resources Index
Chapter 2: Teacher Professionalism, Distributed Leadership, and Peer Coaching
Appendix A: SWEL Support Tool
Chapter 3: The SWEL Model of Academic Language Instruction
- Appendix B: Building Leveled Academic Language Objectives
- Appendix C: Word-Level Academic Content Form
- Appendix D: Sentence-Level Academic Content Form
- Appendix E: Discourse-Level Academic Content Form
- Academic Language Demands Inventory
- Academic Language Video Lecture
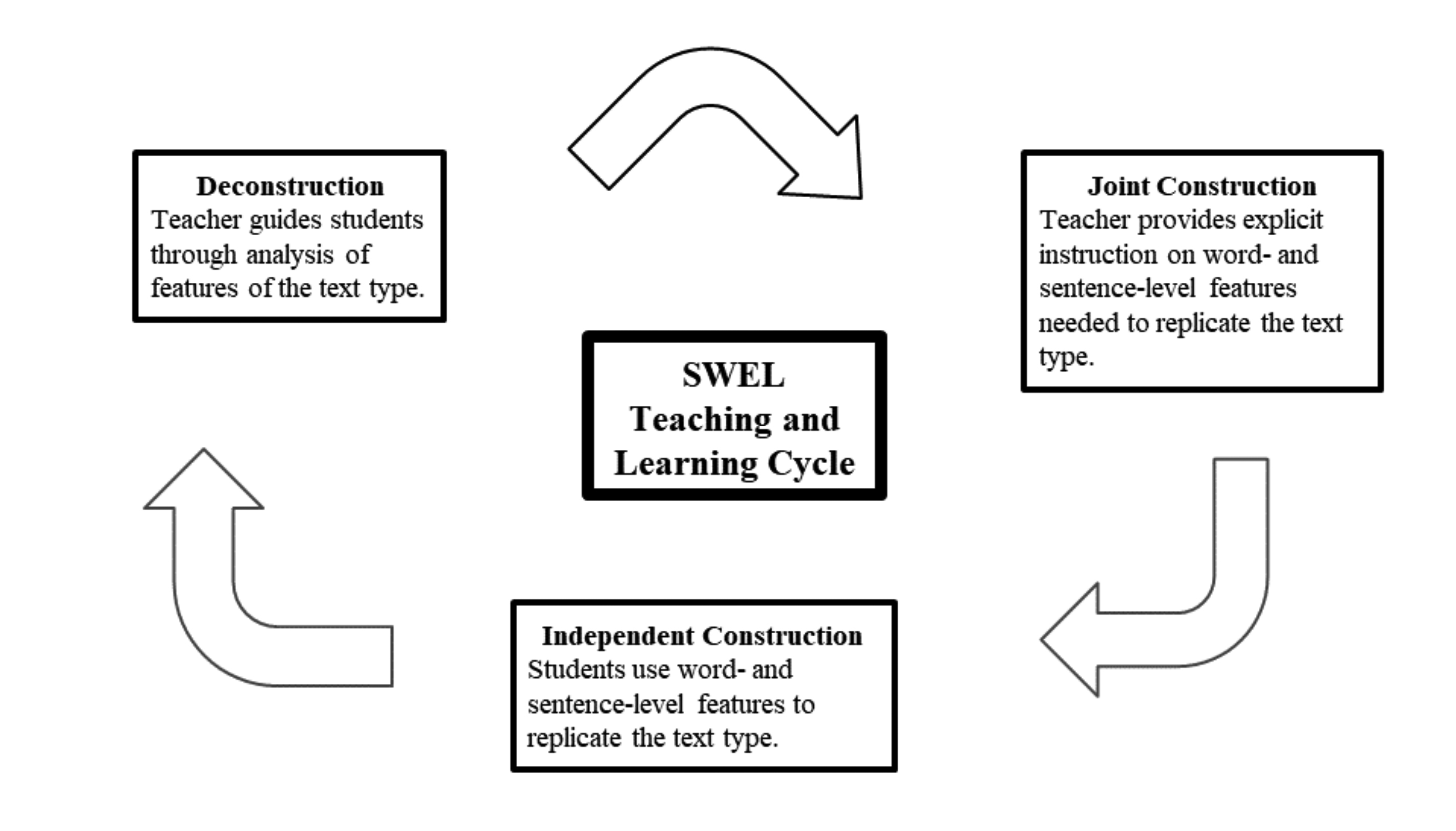
- Figure 1. SWEL Teaching and Learning Cycle
Part B. Application of Teacher Professional Development of Dispositions, Knowledge, and Skills: Professional Development Plans
Chapter 4: Teacher Dispositions Needed to Effectively and Respectfully Serve English Learners
Educators Empathize With Circumstances Related to Immigration
Educators Are Culturally Sensitive and Sustaining
- Handout: I didn't know - Think Pair Share
- Video: Making Sure Each Child Is Known
Educators Believe That Marginalization and Oppression Affect the Educational Experiences of English Learners
- Handout: Critical Incidents in Immigrant Education
- Critical Incidents in Immigrant Education Activity Teacher Trainer Guide
Educators Support Their Students’ Home Language Development
- Article: Getting to Know Your ELLs: Six Steps for Success
- Video: I CAN'T SPEAK MY MOTHER TONGUE (Music Video) - Fung Bros ft. Dough-Boy
- Video: What to Do First in the ELL Classroom
- Handout: Getting to Know the ELs in Your Classroom
- Video: Importance of Students’ Home Languages
- Handout: Crafting School Language Policies
- Article: Classrooms Need to Reflect the Different Home Languages of Students
Educators Recognize the Challenges of Learning English and Content Simultaneously
- Printout: Vowel Sort Cards
- Vowel Sort Answer Key
- Image: My Morning Routine

Image by Ryan McGuire from Pixabay
Educators Are Committed to Ongoing Professional Development
Chapter 5: Teacher Knowledge Needed to Effectively and Respectfully Serve English Learners
Educators Know About Second Language Acquisition and Approaches to Teaching Language Through Content
- Video: Stages of Second Language Acquisition: ESL, ELL, LEP & Bilingual
- Handout: ELD Matrix of Grammatical Forms
- Handout: Five Stages of SLA Activity Sheet
- Handout: Vitamin D Passage
- Handout: Content Area Language Challenge
Educators Know About Approaches to Supporting First Language Literacy
- Guide: Translanguaging: A CUNY-NYSIEB Guide for Educators
- Video: Andy Brown Translanguaging A multilingual Learning
- Video: Session 5: Classroom Examples
- Article: Why Bilinguals Are Smarter
- Article: MIT Scientists Prove Adults Learn Language to Fluency Nearly as Well as Children
- Infographic: 10 Amazing Benefits of Being Bilingual
- Article: Bilingualism: What Happens in the Brain?
Educators Know About the Theories of Cultural Relevance and Sustainability
- Video: Funds of Knowledge
- Handout:Funds of Knowledge Activity Sheet
- Handout: Funds of Knowledge Plan
- Handout: Windows and Mirrors Activity Sheet
- Article: Curriculum as Window and Mirror
Educators Know Who Immigrants Are and How Immigration Happens
- Video: Hand Model of the Brain
- Video: Animated Map Shows History Of Immigration To The US
Educators Know Systems of Oppression and How They Affect the Educational Experiences of Els
- Handout: What I Should Have Said
- Video: Standing Up: What Is Calling in vs. Calling Out?
- Video: Students Learn a Powerful Lesson About Privilege
- Video: What Is Privilege?
- Video: Why Does Privilege Make People So Angry? | Decoded | MTV News
Handout: Understanding Privilege Reflection
Educators Know Approaches to English Learner Advocacy and the Legal Requirements for Adequately Serving English Learners
- Article:ABC's of Family Engagement: Key Considerations for Building Relationships With Families and
- Strengthening Family Engagement Practices
- Article: An Evening With ESL Parents: A Framework for an Orientation Program
- Handout: Influential Court Cases Summaries
Chapter 6: Teacher Skills Needed to Effectively and Respectfully Serve English Learners
Educators Can Plan for Academic Language Instruction
- Profession Cards
- Image: Mulberry Street, New York City

Image from Wikipedia. - APPENDIX B: Building Leveled Academic Language Objectives tool
Educators Can Teach and Assess Academic Language
- Handout: Venn Diagram Listening Activity
- Video: Said Salah Ahmed: The Lion’s Share in Somali
- Handout: Plargs Quiz
- Plargs Vocabulary Cards
- Plargs Quiz Answer Key
Educators Can Differentiate for English Learners
- Handout: Modality Audit
- WIDA Can-Do Descriptors
- Video: WIDA Can-Do Philosophy
- WIDA Can-Do Name Charts
Educators Can Support First Language Literacy
- Guide: Translanguaging: A CUNY-NYSIEB Guide for Educators
- Handout: Dispelling the Myth of “English Only”: Understanding the importance of the First Language in Second Language Learning
Educators Can Support First Language Literacy
Handout: Issues that Impact ELs
Educators Can Enact Culturally Relevant Practices
- Handout: English Learner Profile Template
- Handout: Sample English Learner Profile
Part C. Application of Peer Coaching Using a Directed, Cyclical Approach
Chapter 7: Setting Up Teachers for Success
Part D. Putting SWEL to Work in Your School: Setting the Stage With Intentional Planning
Chapter 8: Drafting an Annual SWEL Action Plan
Appendixes
- Appendix A: SWEL Support Tool
- Appendix B: Building Leveled Academic Language Objectives
- Appendix C: Planning for Word-Level Academic Language Guide
- Appendix D: Planning for Sentence-Level Academic Language Guide
- Appendix E: Planning for Discourse-Level Academic Language Guide
- Appendix F: The SWEL Lesson Plan Inventory
- Appendix G: School-Wide English Learning (SWEL) Action Plan
